How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both recreational and professional users. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced flight modes, camera operation, and legal considerations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone navigation, ensuring you gain the confidence and knowledge to fly responsibly and capture stunning aerial footage.
Understanding the technology and adhering to regulations are key components to a successful and enjoyable drone experience.
We will delve into the essential aspects of drone piloting, demystifying the complexities of flight controls, camera settings, and maintenance procedures. From mastering basic maneuvers to understanding advanced flight modes and navigating legal requirements, this guide equips you with the comprehensive knowledge needed for safe and responsible drone operation. We’ll cover troubleshooting common issues and provide practical tips to enhance your aerial photography skills.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring both the safety of the drone and those around it. This involves several key steps to mitigate potential risks and ensure a smooth flight operation. Neglecting this process can lead to accidents, damage to the drone, or even injury.
Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection includes verifying the drone’s battery level, inspecting the propellers for any damage or wear, and checking the strength of the GPS signal. Battery health is paramount; a low charge can lead to unexpected power loss mid-flight. Damaged propellers can cause instability and loss of control. A strong GPS signal ensures accurate positioning and safe return-to-home functionality.
Pre-Flight Safety Check
The pre-flight safety check is a systematic process designed to identify and address potential hazards before takeoff. This includes checking the surrounding environment for obstacles, assessing weather conditions, and ensuring that the flight area is clear of people and animals. Understanding local regulations and airspace restrictions is also essential.
Pre-Flight Checklist
| Item | Check | Notes | Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Sufficient charge? | Minimum 20% recommended for safe operation. | Charge if necessary. |
| Propeller Inspection | Damage or wear? | Look for cracks, bends, or missing pieces. | Replace damaged propellers. |
| GPS Signal Strength | Strong signal? | Ensure at least 5 satellites are acquired. | Relocate to an area with better GPS reception if needed. |
| Environment Check | Obstacles, weather, people? | Assess for potential hazards. | Clear the flight area. |
| Calibration | IMU and Compass calibrated? | Ensure accurate flight performance. | Calibrate if necessary, following manufacturer’s instructions. |
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is vital. Loss of signal can be addressed by activating the return-to-home (RTH) function, if available. Unexpected malfunctions, such as motor failure, require immediate landing attempts, prioritizing safety. Familiarize yourself with your drone’s specific emergency procedures detailed in the user manual.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section covers basic controls, different control schemes, and best practices for takeoff, landing, and navigation.
Basic Drone Controls
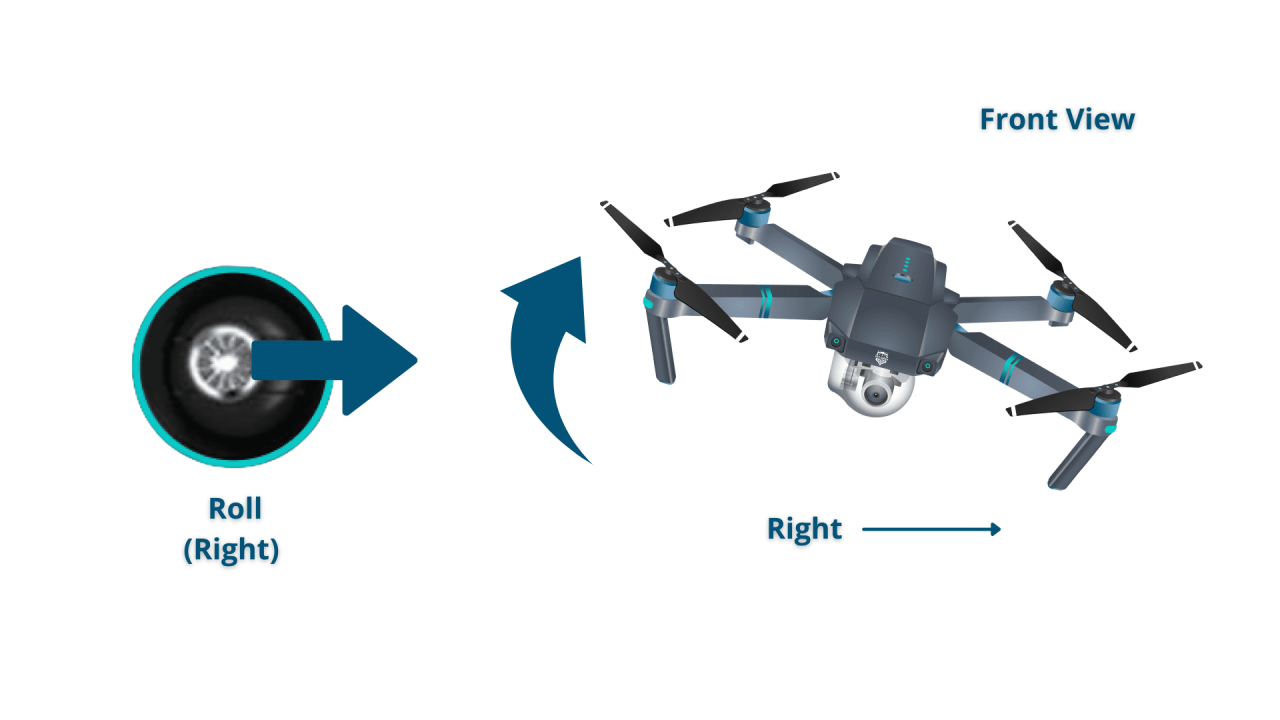
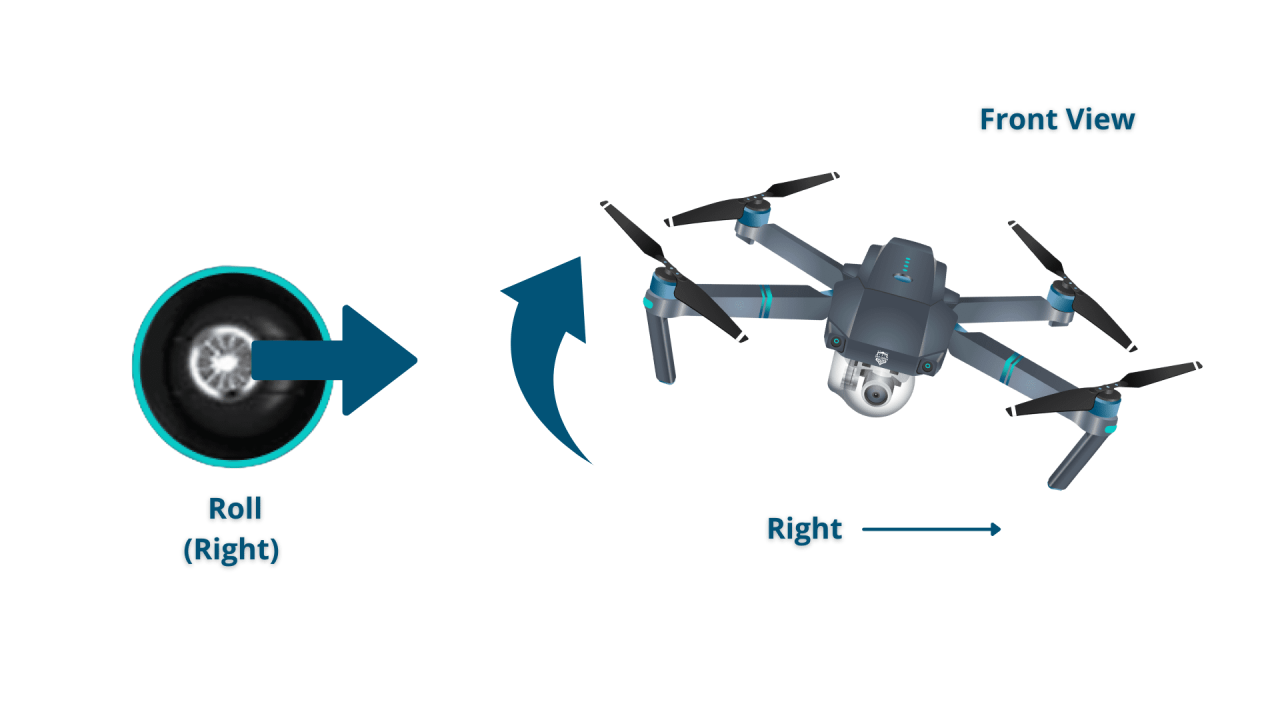
Most drones utilize four primary controls: throttle (altitude), yaw (rotation), pitch (forward/backward tilt), and roll (left/right tilt). Understanding how these controls interact is crucial for precise maneuvering. Throttle controls the drone’s ascent and descent, yaw controls its rotation around its vertical axis, pitch controls movement forward and backward, and roll controls movement left and right.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to ensure safe and responsible operation.
Ultimately, proficient drone piloting comes with practice and a commitment to learning best practices.
Drone Control Schemes
Two common control schemes exist: Mode 1 and Mode 2. Mode 1 uses the left stick for throttle and yaw, and the right stick for pitch and roll. Mode 2 reverses these assignments. The choice depends on personal preference and prior experience with RC equipment. Consistent use of a single scheme is recommended.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures, How to operate a drone
- Perform pre-flight checks.
- Ensure a clear, open space.
- Slowly increase throttle for takeoff.
- Maintain stable hover before maneuvering.
- For landing, slowly decrease throttle.
- Gently set down the drone.
GPS and Visual Navigation
GPS assists in maintaining position and allows for autonomous functions like return-to-home. However, relying solely on GPS can be risky. Visual cues are equally important for obstacle avoidance and precise navigation, especially in areas with weak GPS signals or complex environments. Always maintain visual contact with your drone.
Flight Modes and Settings
Most drones offer various flight modes tailored to different skill levels and situations. Understanding these modes and adjusting settings appropriately is key to safe and effective operation.
Drone Flight Modes
Beginner mode often limits speed and responsiveness, enhancing stability for new pilots. Sport mode unlocks higher speeds and greater maneuverability, suitable for experienced users. Other modes might include GPS-assisted flight, follow-me mode, and cinematic modes for smoother camera movements.
Adjusting Drone Settings
Altitude limits prevent accidental high-altitude flights. Return-to-home (RTH) ensures the drone automatically returns to its takeoff point in case of signal loss. Emergency stops provide immediate control over the drone, bringing it to a halt. These settings should be adjusted based on the flight environment and pilot experience.
Flight Mode Comparison

| Flight Mode | Description | Suitable Conditions | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Limited speed and responsiveness. | Training, confined spaces. | Limited maneuverability. |
| Sport Mode | High speed and responsiveness. | Open areas, experienced pilots. | Increased risk of accidents. |
| GPS Mode | GPS-assisted stability and positioning. | Open areas with good GPS signal. | Vulnerable to GPS interference. |
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture: How To Operate A Drone
Capturing high-quality photos and videos requires understanding and adjusting camera settings. This section explores camera settings, shooting modes, and techniques for stabilizing footage.
Camera Settings Adjustment
ISO controls image sensitivity to light; higher ISO values are better for low-light conditions but can introduce noise. Shutter speed determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light; faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur. Aperture controls the amount of light entering the lens, affecting depth of field.
High-Quality Photo and Video Capture

Different shooting modes, such as time-lapse, slow-motion, and burst mode, offer creative possibilities. Experimentation helps determine the best settings for specific situations. Proper framing and composition are essential for visually appealing images. The rule of thirds and leading lines are useful compositional guidelines.
Footage Stabilization
Minimizing camera shake is crucial for smooth videos. Many drones offer electronic image stabilization (EIS), which digitally corrects for minor movements. Mechanical image stabilization (gimbal) provides more effective stabilization, particularly for more aggressive maneuvers.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Post-flight procedures and regular maintenance are vital for extending the lifespan of your drone. This section Artikels safe landing, post-flight checks, and routine maintenance tasks.
Safe Landing and Power Down
- Slowly descend to a safe landing area.
- Gently set down the drone.
- Power off the drone and remove the battery.
Post-Flight Checks
- Inspect the drone for any damage.
- Check the propellers for wear and tear.
- Verify the battery level and charge if necessary.
- Clean any debris from the drone.
Routine Maintenance
Regular cleaning removes dirt and debris that can affect performance. Proper battery care involves storing them in a cool, dry place at around 50% charge to prolong their lifespan. Avoid extreme temperatures and overcharging.
Drone Storage
Store the drone in a dry, secure case or bag, protecting it from dust, moisture, and physical damage. Keep batteries separate from the drone to avoid accidental short circuits. Accessories should also be stored in a way that prevents damage or loss.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local laws and regulations. This section highlights key aspects of drone legality.
Drone Regulations
Regulations vary by region. Some jurisdictions require drone registration, while others have specific airspace restrictions and no-fly zones (e.g., near airports, sensitive infrastructure). Always check with your local aviation authority for specific rules and regulations before flying.
Drone Registration
Drone registration involves providing information about your drone and yourself to the relevant authority. This allows for tracking and accountability in case of accidents or misuse. Failure to register can result in penalties.
Airspace Restrictions
Many areas have designated no-fly zones to protect sensitive locations or ensure aviation safety. These areas are typically marked on online maps or apps. Flying within these zones can result in fines or legal action.
Penalties for Violations
Penalties for violating drone regulations can range from warnings and fines to legal prosecution, depending on the severity of the violation. Always prioritize safe and legal operation.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite careful preparation, issues can arise. This section provides troubleshooting steps for common drone problems.
Common Drone Malfunctions
Low battery, GPS signal loss, and motor problems are among the most common issues. Understanding potential causes and troubleshooting steps can minimize downtime and prevent further damage.
Troubleshooting Table
| Problem | Possible Causes | Troubleshooting Steps | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Insufficient charge, high power consumption. | Charge battery, reduce flight time. | Regularly check battery level, use efficient flight patterns. |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructions, weak signal. | Relocate to an area with better GPS reception, use RTH function. | Fly in open areas with strong GPS signal. |
| Motor Problems | Motor damage, loose connections. | Inspect motors and connections, seek professional repair. | Regularly inspect motors and connections. |
Seeking Professional Assistance
If troubleshooting steps fail to resolve the issue, it’s best to seek professional assistance from a qualified drone repair technician. Attempting complex repairs without proper knowledge can cause further damage.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of technical skill, responsible practice, and a deep understanding of safety regulations. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to embark on your drone piloting journey with confidence. Remember that continuous learning and adherence to best practices are vital for maintaining a safe and enjoyable experience, both for yourself and those around you.
Safe flying!
Key Questions Answered
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to help you get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This will provide you with the necessary knowledge to safely and effectively control your drone, ensuring a positive flying experience.
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and autonomous flight modes. Look for models with clear instructions and readily available support.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations. Generally, it’s best to avoid completely depleting the battery and to charge it after each flight to maintain optimal performance and lifespan.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If the signal is lost, the drone should automatically return to its takeoff point. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
How do I obtain permission to fly in restricted airspace?
Check with your local aviation authorities for airspace restrictions and any necessary permits or approvals before flying. Unauthorized flights can result in penalties.